
So I will write it isn't possible to definitively write about atomic radius - but (and I don't know how you measure it) the wave-function probablistic "there isn't a definitive radius" approach is maybe the most soundĪnd click around for different electron density plots for different orbitals to try and visualise this idea of electron probability density. Logic and Solution: The reported radii of noble gas elements are van der Waals radii, which are 40 more than the actual atomic radii. Therefore the order of atomic radii or diameter of the given Halogens is F < Cl < Br

From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, " 1) nonmetallic properties and atomic radius. The atomic radius of fluorine and neon is 0.75 angstrom and 1.60 angstrom respectively. From the angles and intensities of these scattered beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal.
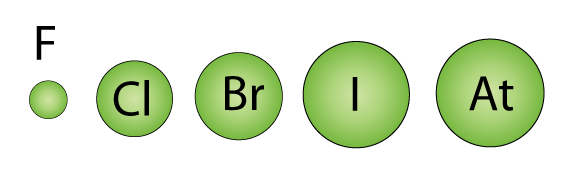
(from wiki) X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and scatters into many different directions. That is, we cannot point to a region or space where the atom ends and hence determine a radiusĢ) If the atoms are in a 3D ionic (or other crystalline) lattice we can use X-ray diffraction to determine accurately inter-ionic distance In moving from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases as the effective nuclear charge increases. (wiki orbital)" This (atomic orbital) function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus" Does oxygen have a larger atomic radius than fluorine Atomic radii of oxygen is 48 pm. Loss of an electron from an atom results in the. Isn't a problem here about defining what the radius of an atom is?ġ) If we consider an isolated atom and we accept that the electrons are in fixed energy levels but that In the solid-state, for example, the internuclear distance between two adjacent chlorine atoms of two nearby molecules is 360 pm. This the ionic radius of fluoride ion (F) is 136 pm whereas atomic radius of Fluorine (F) is only 64 pm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
